Concepts¶
Project¶
A project is the main entity of ProjeQtOr.
Project element is more than a planning element.
It is also used to allow gathering all data depend on project:
Risk management: mitigation, reserve
Ticketing: Issue, Bug tracking, Change request, Support
Steering: Steering, Decisions, Action plan
Expense and Incomes: project expenses, individual expenses, activities expenses, Order, Bill, Payment…
Allows restricting data visibility to users by project.
The project data visibility is granted according to the user profile.
See also
Project selector¶
The project selector works as a filter.
By default, the selector displays “all projects”, you can change this view in the user parameters and choose the project to display by default.
You can restrict data for one or more dedicated projects without necessarily being bound.
See also
Project’s type¶
Four project types can be defined:
Operational project¶
Code: OPE
Most common project to follow activities.
A project can be non billable, used for internal or administrative project for example or billable project
You can choose the invoice type associated with each project among : manual Billed, fixed price, capped time, time & materials, internal.
Administrative project¶
Code: ADM
Allows to follow the non productive work as holidays, sickness, training, …
All resources have access to this project type without being allocated (Project) or assigned (Activity).
Create an activity, like an OPE project, for each type of absence.
See also
Template project¶
Code: TMP
Designed to define models to be copied into an operational project.
Any project manager (profile) can see and copy these projects without having to be assigned to them. To edit this template project directly, an assignment is required.
To modify it without assignment, you must first copy the project into an operational type project (OPE).
A model project, even if it is displayed in the Gantt chart, is not taken into account in planning. Even if there are assignments and assigned load, it is not stored and therefore is not planned.
You will not be able to display the planning detail on template type projects.
See also
Proposal project¶
Code: PRP
Proposal-type projects are intended to identify strategic projects. It allows you to define objectives based on internal and external factors to achieve them.
For projects of this type, 4 additional fields are displayed:
Strength
Weakness
Opportunity
Threat
Strategic value is mandatory.
The project is automatically saved as “Under construction” and is read-only.
See also
Allocation to project¶
Allocation to project is used to:
Define project data visibility with access right.
Define resource availability.
Define the period of access to project data by the user.
You can select user, resource or contact.
if the selected contact is also a resource, then it will be displayed in the assignment table at the resource level.
User and contact allocation¶
Allocation to project can be defined on Project and Users screen.
The selected profile allows you to define the rights on all the elements of the project.
The profile displayed first will be the default but the profile given to an assignment may be different on each project.
These rights only apply to the selected project. If a sub-project is created on it then the rights will be automatically inherited.
You can change the profile on any project at any time.
The period selection allows you to define the visibility period of the project data. It can be used to limit the access period, in accordance with the service agreement.
Note
Profile defined in allocation to project does not grant or revoke access to users.
General access to application functionalities and data is defined by default user profile.
Resource allocation¶
Allocation to project allows to define the resource availability on project.
A resource may be allocated to projects at a specified rate for a period.
Allocation to project can be defined on Project and Resource screens.
You can also allocate a team or an organization to a project in Teams and Organization screens.
Note
A resource allocated to a project can be defined as responsible of project items treatment.
Period & Rate¶
A resource may be allocated to a project at a specified rate for a period.
This rate is used to keep some scheduling time for other tasks.
For example, if the allocation rate is 50%, the resource whose weekly calendar is 5 days (Monday to Friday) will not be scheduled more than half of this calendar, therefore 2.5 days per week.
If the period is not specified then the resource is allocated throughout the project.
Warning
The planning calculator tries to plan, the remaining work on the task assigned to a resource within the allocation to project period.
If remaining work on the task can’t be planned, a purple bar appears in the Gantt view.
Change resource¶
A resource can be changed on allocation to project.
All tasks assigned to old resource will be transferred to the new resource with planned work and remaining work.
Work done on tasks belongs to always the old resource.
Multi-allocation¶
A resource can be allocated to multiple projects in the same period.
In the section Allocations in Resource screen, a tool allows to displayed conflicts.
Tip
How resolve conflicts?
You can change allocation period to avoid overlap between projects.
You can change the rate of allocation for it does not exceed 100% for the period.
Activity¶
An activity is a kind of task that can be planned or that groups other activities.
This is usually a long-term task that can be assigned to one or more resources.
Activities will appear on the Gantt schedule view.
You might consider an activity as:
Planned tasks,
Modification requests,
Some phases,
Versions or new deployments,
Activities can be grouped as a Mother / Daughter link. The parent activity must belong to the same project.
A WBS structure is applied and a dynamic index is calculated for all activities and it can be changed in the Gantt planning view using drag and drop.
An activity can be linked to elements that cannot be planned like tickets, so that the time spent on tickets can be taken into account in the overall planning of the project. This option allows you to assign a time pool that will be scheduled and to link tickets to this tank. The time spent on tickets will then be decremented to that of the planning activity.
See also
Assignment¶
The assignment is used to assign resources to project tasks (activity, test session, meeting). Only resources allocated by the project can be assigned to project tasks.
It consists to assign a resource to a task in a specific function and contains data about work on task, planned, real, left and reassessed work.
You keep track of the resources that have been assigned and worked on the activity.
You can define a period for the resource on each of the activities.
You can also define an assignment rate for each activity that will determine the daily planning based on the percentage of its FTE.
Important
Basic, you cannot delete a resource assignment after the resource has entered actual work on the activity.
This assignment can be deleted by a profile including the option “Can delete items with real work” in the access rights menu in the specific acces.
Similarly, if the resource has completed its activity, deletion is not possible.
Organization¶
The notion of organization introduces a way to consolidate projects on a different hiererchic structure, apart from projects / sub-projects structure.
It defines the structure of the company in the frame of organizations: departments, units, location, …
The organization summarizes the data of the projects in progress for the organization.
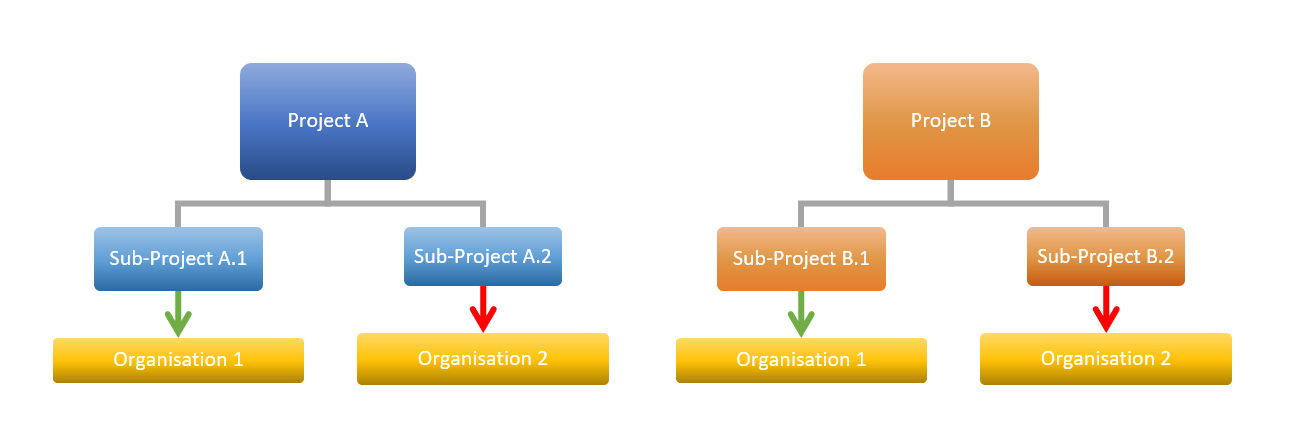
distribution within organizations¶
Each project can be linked to an organization and resources can be linked to an organization.
Note
Depending on the profile, you can limit the visibility of resources to people in the same organization or team as the current user.
Sub-projects are by default attached to the same organization as the parent, but can be integrated into another organization.
Product¶
A product can be a material object or for IT/IS projects is a software application.
It can have a complex structure that can be composed of sub-product and components and its components can have several versions that represent each declination.
A product is an element delivered by a project.
Several element can identified a product and/or a product version. Documents themselves can be identified to products.
The link with the project have no impact on project planning. It indicates only that project is devoted to a specific product versions.
The link management is done on Project and Product version screens.

Link with projects¶
Product structure¶
The product structure is defined depending on the relationships defined between product and component elements.
The rules defining a product structure are:
Relationships between…¶
…product elements¶
A product can have several sub-products.
A sub-product can be in the composition only one product.
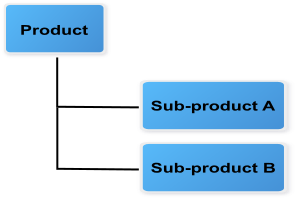
Relationships between product elements¶
… product and component elements¶
- A product can be composed of several components.
A component can be in the composition of several products.
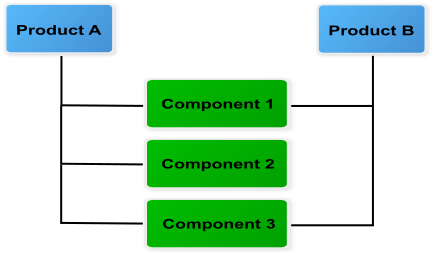
Relationships between product and component elements¶
… component elements¶
Components can be linked between them (N to N relationships).
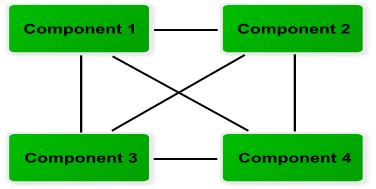
Relationships between component elements¶
Versions of product and component elements¶
A product can have several versions that represent each declination of product.
A component can have several versions that represent each declination of the component.
Links can be defined between versions of products and components, but only with the elements defined in the product structure.
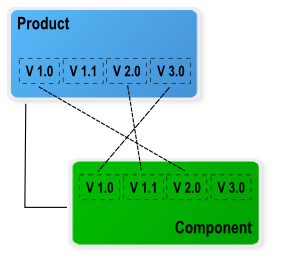
Link between versions of product and component¶
Planning¶
ProjeQtOr implements work-driven planning method based upon on resource availability and their capacity.
Resource availability is defined by calendars and project allocation period.
Each resource is attached to a calendar to define its working days and tasks assigned to the resource will be planned according to working days defined in the calendar.
Resource capacity (FTE) is defined on daily base and the planning tool does not exceed the daily resource capacity.
See also
The project allocation rate is used to resolve allocation conflicts between projects and allows to define resource availability for a project during a period. Use with the resource capacity, it allows to define the project allocation capacity on a weekly base.
The task assignment rate is used to keep some scheduling time each day for other tasks. Use with the resource capacity, it allows to define the assignation capacity on a daily base.
Planning elements¶
ProjeQtOr offers standard planning elements like Project, Activity and Milestone but also, two more planning element: Test session and Meeting.
Project¶
This planning element defines the project.
It allows to specify information on the project sheet like the customer, bill contact, sponsor, manager and objectives.
Sub-project is used to split the project, to correspond the organizational breakdown or something else by instance.
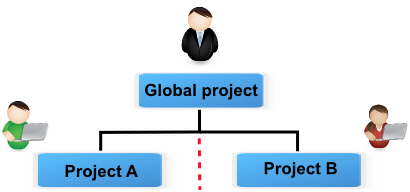
Separation of duties¶
Documents, notes and attachments can be annexed.
A project leader and team can be allocated to each sub-project.
Project allocation allows to define data visibility and isolate sub-projects.
See also
Activity¶
This planning element can be a phase, a delivery, a task or any other activity.
An activity can grouped other activities or be a task. This allows to define the structure of phases and deliveries.
Dates, works and costs of activities (child) are summarized in the activity (parent).
A task is assigned to resources for to be performed.
See also
Test session¶
This planning element is a specialized activity aimed for tests.
A test session allows to define a set of test case that must be run to meet a requirement.
It can grouped other test sessions or be a task. This allows to define the structure of test sessions.
Dates, works and costs of test sessions (child) are summarized in the test session (parent).
A task is assigned to resources for to be performed.
See also
Milestone¶
This planning element is a flag in the planning, to point out key dates.
May be a transition point between phases, deliveries.
ProjeQtOr offers two types of milestone floating and fixed.
See also
Meeting¶
This planning element acts like a fixed milestone, but it’s a task.
Like a milestone, a meeting can be a transition point.
But also, like a task because it’s possible to assign resources and planned work.
See also
Dependency¶
Dependencies allow to define the execution order of tasks (sequential or concurrent).
All planning elements can be linked to others by dependencies.
There are several types of dependencies that allow to start and/or finish before/after another element.
Dependencies can be managed in the Gantt chart and in screen of planning element.
A delay can be defined between predecessor and successor.
Planning mode¶
Planning mode allows to define constraints on planning elements: activity, test session and milestone.
Milestones planning mode¶
Planning modes are grouped under two types for milestone :
Floating
These planning modes have no constraint date.
Planning element is floating depending on its predecessors.
Fixed
These planning modes have constraint date.
Planning elements planning mode¶
Several planning modes for your project elements are proposed to best manage the time spent on certain planning elements.
As soon as possible
Work together
Fixed duration and parent activity
Constraint duration
Must not start before validated start date
Must start at validated date
Should end before validated end date
Regular between dates
Regular in full days
Regular in half days
Regular in quarter days
Recurry (on weekly basis)
Manual planning
Note
You can set the default scheduling mode for an item from its type
Planning priority¶
Planning items are scheduled in this priority order:
Manual planning
Dependency
Fixed date
Recurring activities
Fixed duration
Others
You can also fill in the priority field in the management section of your planning items to define a different planning order than the default. Possible values are from 1, for the highest priority, to 999, for the lowest priority.
See also
Planning order fore more details
Note
If projects have different priorities, all elements of project with highest priority are planned first.
Project structure¶
Work breakdown structure (WBS) is used to define project structure.
Breakdown can be done with sub-projects, activities and test sessions.
Structure management
As seen previously, the project can be split in subprojects.
All other planning elements concerned by the project or subproject are put under them without structure.
Planning elements can be grouped and orderly in hierarchical form.
Structure management can be done in the Gantt chart or in planning elements screen.
WBS element numbering
The project is numbered by its id number.
All other elements are numbered depending on their level and sequence.
WBS numbering is automatically adjusted.
Project planning calculation¶
The project planning is calculated on the full project plan that includes parents and predecessor elements (dependencies).
The calculation is executed task by task in the following order:
Manual Planning
Dependencies (Predecessor tasks are calculated first)
Prioritized planning elements
Project priority
Task priority
Project structure (WBS)
The remaining work (left) on tasks will be distributed on the following days from starting planning date, taking into account several constraints:
Resource availability and capacity
Project allocation capacity (Project allocation rate)
Assignation capacity (Task assignment rate)
Planning mode
Resource overloads
This is not possible to overloading the resources.
The planning calculation process respects availability and capacity of the resource.
If it is not possible to distribute remaining work, on already planned days, the calculation process uses new available time slot.
Draft planning¶
Two methods can be used to create a draft planning.
Use planning mode “fixed duration”
This planning mode is used to define fixed duration tasks. See: Planning modes
Dependencies allow to define the execution order of tasks. See: Dependencies
You can define this planning mode as defaut in the Activities Types screen for some types of activities you’ll use in draft plannings
Use faked and team resource
The faked and team resource can be useful to get a first estimate of project cost and duration without involving the real resources.
Planning schedule is calculated using of the work-driven planning method.
Faked and team resources can be mixed in same draft planning.
Faked resources
For instance, you want to define a Java developer resource. You can create a resource named “Java developer #1”.
There are several levels of Java developer with different daily costs (beginner, intermediary and expert).
You can define for this resource the functions and average daily cost for each level. (See: assigment)
You assign this resource to tasks, to a specific function (level). (See: assignment)
Faked resource will be easily replaced with real resources when project becomes real, with allocation replacement feature
 .
.
Team resource
A team resource is a resource whose daily capacity has been defined to represent capacity of a team (Capacity (FTE) > 1).
For instance, you needed to define four Java developers, but you don’t want to create a resource for each. You can overload the daily capacity of the resource (Example: Capacity FTE=4).
Using team resources is very easy but renders estimation of project duration as draft, not taking into account constraint of different resources such as possibly different skills or expertise level.
With team resources it is very easy to estimate planning with different number of members in the team : what if I include 5 Java develpers instead of 4 ? Just change capacity to 5 and re-calculate planning…
ProjeQtOr roles¶
A stakeholder can play many roles in ProjeQtOr.
Specific roles are defined to allow:
To categorize the stakeholders involved in the projects.
To identify the stakeholders on items.
To regroup the stakeholders to facilitate information broadcasting.
Profiles definition¶
The profile is used to define in-app permissions and data access rights.
Each resource, user or contact is assigned a profile. This is mandatory. This is the default profile.
Multiple resources, users, or contacts can have the same profile. They are linked to a profile and belong to this group and share the same application behavior.
The profile is used to define access rights to application and data, first.
Also, the profile is used to send message, email and alert to groups.
See also
Profils and Access rights
A profile can be selected to a user, resource or contact in project allocation.
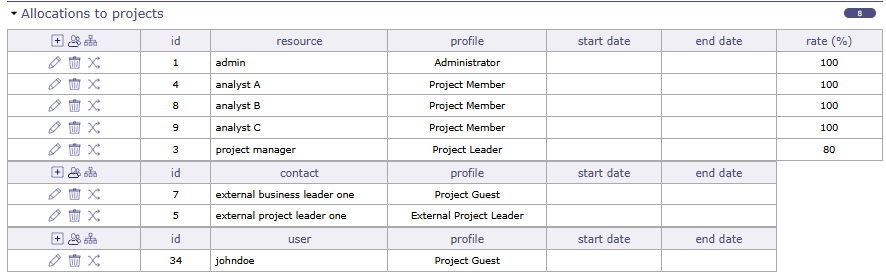
Profiles allocation to the project¶
The profile selected is used to give data access to elements of the projects.
A resource can have a different profile on each project to which it is assigned.
The profile is used to define who can change from one status to another one.
You can restrict or allow the state transition to another one according to the profile.
See also
Workflow screen.
Predefined profiles¶
ProjeQtOr offer some predefined profiles.
Administrator profile
Only these users can manage the application and see all data without restriction.
The user “admin” is already defined.
Supervisor profile
Users linked to this profile have a visibility over all the projects.
They cannot create or modify any element.
This profile allows to monitor projects.
Project leader profile
The project leader has a complete access to owns projects.
Project member profile
A project member is working on projects allocated to it.
The user linked to this profile is a member of team projects.
Project guest profile
Users linked to this profile have limited visibility to projects allocated to them.
The user “guest” is already defined.
ProjeQtOr allow to involve client employees in their projects.
The distinction between this profile and its equivalent, user access is more limited.
Stakeholder definition¶
ProjeQtOr makes it possible to define the roles of the stakeholders.
The definition of stakeholders is done in part with the profile and with the definition of user / resource / contact. This allows certain access and visibility rights to be determined.
These combinations are used to define:
Connection to the application.
Data visibility.
Availability.
Roles.
These stakeholders can be either resource, contact, or users, and they can also be all three.
profile
To a user, interface and data visibility is based on its user profile.
User profile defined general access to application functionalities and data.
Only resource can be planned on a planning element.
ProjeQtOr allows to involve contacts in projects.
Access rights
Defined if a user has access to own projects or over all projects.
Access right on all project is typically reserved for administrators and supervisors. They have access to all elements of all projects.
Shared data
For a stakeholder, data on user, resource and contact are shared.
Allocation to project and user profile are also shared.
Tip
For a stakeholder, you can define and redefine the combination without losing data.
Resource function and cost¶
Function¶
The function defines the generic competency of a resource.
It is used to define the role play by the resource on tasks.
In real work allocation screen, the function name will be displayed in the real work entry.
A main function must be defined to resource and it is used as default function.
A daily cost can be defined for each function of the resource.
See also
Functions screen allows to manage function list.
Resource cost definition¶
Allows to define the daily cost, according to the functions of the resource.
The daily cost is defined for a specific period.
When real work is entered, the real cost is calculated with work of the day and daily cost for this period.
When the project planning is calculated, resource cost is used to calculate planned cost.
Planned cost is calculated with planned work of the day and current daily cost.
See also
Function and cost are defined in Resource screen.
Resource calendar¶
A calendar defines the working and off days in a the year.
You can define as many calendars as needed. Each resource is attached to a calendar.
Calendars are used in the planning process which dispatches work on every working day. Working days defined in a calendar allows to show availability of resources.
During the planning process, the assigned work to a resource is planned in its working days.
The default calendar is used to define the working days in the year. By default, this calendar is defined for all resources.
Warning
You must re-calculate an existing planning to take into account changes on the calendar.
Contexts¶
The contexts defines a list of elements selectable to define ticket context and test case environment.
Contexts are initially set to be able to define contexts for IT Projects, for three context types :
Environment
Operating System
Browser
They can be changed to be adapted to any kind of project.
